Why is CCl4 soluble in water?
Think of it like this: oil and water don’t mix. Oil is non-polar, and water is polar. Just like oil and water, CCl4 and water don’t mix because their molecular structures are incompatible. They don’t have a strong enough attraction to pull each other apart and dissolve.
Here’s a deeper dive into the chemistry behind why CCl4 isn’t soluble in water:
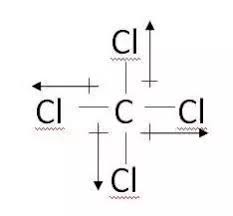
Polarity: The difference in electronegativity between carbon and chlorine in CCl4 is not significant enough to create a dipole moment. This means that the electrons are shared fairly evenly between the carbon and chlorine atoms, making the molecule non-polar.
Hydrogen Bonding: Water molecules are highly polar and form strong hydrogen bonds with each other. These bonds are responsible for water’s high boiling point and surface tension. CCl4, lacking the ability to form hydrogen bonds, cannot disrupt these strong attractions in water.
“Like Dissolves Like” Principle: This rule states that substances with similar polarities tend to dissolve in each other. Since CCl4 is non-polar and water is polar, they are incompatible and do not dissolve in each other.
In short, CCl4 is not soluble in water because their molecular structures are incompatible due to polarity differences. This incompatibility prevents them from forming the necessary attractions to dissolve.
Is CCl4 soluble in water or hexane?
CCl4 is a non-polar molecule. Hexane is also non-polar. This means that both molecules have similar intermolecular forces, primarily London dispersion forces. These forces are relatively weak, but they are strong enough to hold CCl4 and hexane molecules together in a solution.
On the other hand, water is a polar molecule. It has strong hydrogen bonds between its molecules. CCl4 cannot form these strong hydrogen bonds with water, making it insoluble in water.
Think of it this way: CCl4 and hexane are like two people who share similar interests and can easily understand each other. They can mix and hang out easily. Water is like someone who speaks a different language and has different interests. It just doesn’t mesh well with CCl4.
In summary, the solubility of a substance depends on the types of intermolecular forces present. Non-polar substances like CCl4 and hexane are soluble in each other because they have similar intermolecular forces. Polar substances like water are not soluble in non-polar substances like CCl4 because they have different intermolecular forces.
What happens when CCl4 is mixed with water?
When carbon tetrachloride and water are combined, they form two distinct layers. The carbon tetrachloride, being denser, settles to the bottom, while the water floats on top. This separation happens because carbon tetrachloride is a nonpolar molecule, meaning it has no positive or negative ends. Water, on the other hand, is a polar molecule with a positive end (hydrogen) and a negative end (oxygen).
Think of it like trying to mix oil and water. They don’t mix because their molecular structures are different.
Now, you might be wondering why carbon tetrachloride doesn’t react with water. The answer lies in the types of bonds present in each molecule. Carbon tetrachloride has only strong covalent bonds, while water has strong hydrogen bonds between its molecules.
For a reaction to occur, the oxygen atom in the water molecule would need to form a bond with the carbon atom in the carbon tetrachloride molecule. However, this is highly unlikely because the oxygen atom in water already has a strong hydrogen bond with another water molecule. This makes it very difficult for the oxygen atom to break its existing hydrogen bond and form a new bond with the carbon atom in carbon tetrachloride.
In simpler terms, the hydrogen bonds in water are just too strong for the carbon tetrachloride to overcome. This means that the carbon tetrachloride and water molecules will happily exist side-by-side without reacting.
Why is CCl4 immiscible in water?
Water is a polar molecule, meaning it has a positive and negative end due to the uneven distribution of electrons. Think of it like a tiny magnet. CCl4, on the other hand, is non-polar. Its electrons are evenly distributed, making it neutral.
Now, remember that “like dissolves like”. Polar molecules like water tend to dissolve other polar molecules. Non-polar molecules like CCl4 prefer to hang out with other non-polar molecules. This is why CCl4 and water don’t mix. They are immiscible – they form separate layers.
So what about SiCl4?
You might be wondering why SiCl4 behaves differently. Silicon, unlike carbon, has empty d orbitals. These orbitals can accept the electrons from the oxygen atom in water, leading to a chemical reaction called hydrolysis.
Think of it like this: Silicon’s empty d orbitals are like extra seats on a bus. The oxygen atom from water can hop on and join the party. But carbon’s s and p orbitals are full, so there’s no room for the oxygen atom.
In simpler terms, the empty d orbitals in silicon allow it to form a temporary bond with the oxygen atom in water. This weakens the Si-Cl bonds and makes SiCl4 more susceptible to hydrolysis. Carbon, without those empty d orbitals, can’t participate in this kind of interaction. That’s why CCl4 remains immiscible in water.
Is pentane soluble in water?
Think of it this way: water molecules are like little magnets, with a positive side and a negative side. These magnets attract each other, forming strong bonds. Pentane molecules, on the other hand, are like neutral objects with no magnetic poles. They don’t have the same attraction to water molecules. Because of this, the water molecules stick together, leaving the pentane molecules to form their own separate layer. This is why you see oil and water separate – oil is made up of nonpolar molecules similar to pentane.
The concept of “like dissolves like” is helpful to understand solubility. Polar molecules dissolve in polar solvents, while nonpolar molecules dissolve in nonpolar solvents. Since pentane is nonpolar, it’s not soluble in water, a polar solvent. You’ll need a nonpolar solvent, like hexane or diethyl ether, to dissolve pentane.
Is CCl4 or CH2Cl2 more soluble in water?
The key to understanding solubility lies in the concept of “like dissolves like”. This means that substances with similar polarities tend to dissolve in each other.
CH2Cl2 is a polar molecule. This is because the chlorine atoms are more electronegative than the carbon and hydrogen atoms. This difference in electronegativity creates a partial positive charge on the carbon and hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on the chlorine atoms, resulting in a dipole moment.
On the other hand, CCl4 is a nonpolar molecule. While the chlorine atoms are electronegative, they are arranged symmetrically around the carbon atom. This symmetry cancels out any individual bond dipoles, resulting in a zero net dipole moment.
Water is a highly polar molecule, with a strong dipole moment. Since CH2Cl2 is also polar, it can interact with water through dipole-dipole forces, which are relatively strong intermolecular forces. These forces allow CH2Cl2 to dissolve in water.
CCl4, being nonpolar, cannot form strong dipole-dipole interactions with water. It can only interact with water through weak London dispersion forces (LDFs), which arise from temporary fluctuations in electron distribution. These weak interactions are not strong enough to overcome the strong hydrogen bonds between water molecules, leading to poor solubility.
In summary, CH2Cl2 is more soluble in water than CCl4 because it is a polar molecule that can form strong dipole-dipole interactions with water molecules. CCl4, being nonpolar, can only interact with water through weak London dispersion forces, resulting in much lower solubility.
Why is hexane insoluble in water?
Let’s dive a little deeper. Water molecules are very attracted to each other because of the strong hydrogen bonds they form. Hydrogen bonds are like little magnets that hold water molecules together. When hexane is added to water, the water molecules are too busy holding hands with each other to make room for the hexane molecules. Since hexane molecules can’t form hydrogen bonds with water, they’re left out in the cold, so to speak.
To summarize, the difference in polarity between hexane and water makes them incompatible. Water’s strong attraction to itself leaves no room for hexane, making it insoluble in water.
See more here: Is Ccl4 Soluble In Water Or Hexane? | Is Ccl4 Soluble In Water
Is CCl4 soluble in water?
So why is CCl4 so poorly soluble in water? It all comes down to something called polarity. Water is a polar molecule, meaning it has a slightly positive end and a slightly negative end. Think of it like a tiny magnet! CCl4, on the other hand, is a nonpolar molecule. Its electrons are evenly distributed, so it doesn’t have any distinct positive or negative regions.
Now, here’s the key: polar molecules like to hang out with other polar molecules, and nonpolar molecules prefer the company of other nonpolar molecules. It’s like oil and water – they just don’t mix! Because CCl4 is nonpolar, it doesn’t readily dissolve in polar water.
However, you might be wondering: if CCl4 doesn’t like water, what does it like? Well, it turns out CCl4 is quite happy in the company of other nonpolar molecules. That’s why CCl4 is soluble in solvents like chloroform, benzene, alcohols, ethers, and formic acid. These solvents are all nonpolar, so they can easily form bonds with CCl4.
It’s important to remember that solubility is not just about whether something will dissolve at all. It’s also about how much of it will dissolve. In the case of CCl4, its low solubility in water means that it doesn’t easily mix with water, even though a tiny amount will dissolve. This low solubility has some important implications, especially when it comes to environmental issues. Since CCl4 doesn’t dissolve well in water, it can persist in the environment for a long time, potentially causing harm to living organisms.
What is the solubility of carbon tetrachloride in water?
At 25°C, carbon tetrachloride has a solubility of 1.2 g/L in water. This means that only 1.2 grams of carbon tetrachloride can dissolve in one liter of water at this temperature. Chloroform (CHCl3), on the other hand, is much more soluble in water, with a solubility of 10.1 g/L at 25°C. This means that chloroform is almost ten times more soluble in water than carbon tetrachloride.
Why is this difference in solubility so significant? The answer lies in the nature of the molecules involved and their interactions with water.
Carbon tetrachloride is a nonpolar molecule. This means that its electrons are distributed evenly throughout the molecule, resulting in no significant positive or negative charges. Water, on the other hand, is a polar molecule. Its oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge, while its hydrogen atoms carry partial positive charges.
This polarity difference plays a crucial role in solubility. Polar molecules like water tend to dissolve other polar molecules because they can form strong hydrogen bonds with them. Nonpolar molecules like carbon tetrachloride, however, cannot form these bonds with water, making them much less soluble.
Chloroform, while still nonpolar, has a slightly higher polarity than carbon tetrachloride due to the presence of the hydrogen atom. This slight increase in polarity allows it to interact with water molecules to a greater extent, leading to its higher solubility.
In essence, the difference in solubility between carbon tetrachloride and chloroform highlights the importance of polarity in determining how well substances dissolve in water.
Which is more soluble carbon tetrachloride or chloroform?
At 25°C, chloroform dissolves in water to a concentration of 10.1 g/L, while carbon tetrachloride only dissolves to 1.2 g/L. That means chloroform is almost ten times more soluble in water than carbon tetrachloride. Why is this?
The answer lies in the difference in the intermolecular forces between these two molecules and water.
Intermolecular forces are attractive forces that exist between molecules. These forces are responsible for many of the physical properties of substances, including their solubility.
Chloroform has a dipole moment, meaning one end of the molecule has a slightly positive charge and the other end has a slightly negative charge. This dipole moment allows chloroform to interact with water molecules through dipole-dipole interactions. Water is also a polar molecule, so it can interact with the dipole of chloroform.
On the other hand, carbon tetrachloride is a nonpolar molecule. It doesn’t have a dipole moment, so it can’t participate in dipole-dipole interactions with water. The only intermolecular forces that can exist between carbon tetrachloride and water molecules are weak London dispersion forces.
Since dipole-dipole interactions are stronger than London dispersion forces, chloroform interacts more strongly with water and is therefore more soluble.
In summary:
Chloroform is more soluble in water than carbon tetrachloride because chloroform is a polar molecule with a dipole moment, allowing it to form stronger dipole-dipole interactions with water molecules.
Carbon tetrachloride is nonpolar and only interacts with water through weak London dispersion forces.
Think of it like this: chloroform is like a friendly dog that loves to play with water, while carbon tetrachloride is like a shy cat that prefers to stay away from water.
See more new information: bmxracingthailand.com
Is Ccl4 Soluble In Water? Understanding Polarity And Solubility
Let’s get down to business. CCl4, or carbon tetrachloride, is a fascinating molecule. You might be wondering if it can mix with water like sugar or salt. The answer, my friend, is a resounding no. CCl4 isn’t soluble in water, and here’s why.
The “Like Dissolves Like” Rule
Think of it this way: water is a polar molecule, meaning it has a slightly positive end and a slightly negative end. This makes water a good solvent for other polar molecules like sugar (sucrose).
But CCl4 is a nonpolar molecule, meaning it doesn’t have a positive or negative end. It’s like a balanced seesaw, no leaning or tipping. This is why CCl4 prefers to hang out with other nonpolar molecules like oil.
The Battle of Forces
The “like dissolves like” rule isn’t just a cute saying. It’s based on the tug-of-war between intermolecular forces.
Water uses strong hydrogen bonds to stick together. These bonds are like strong magnets holding water molecules in a tight grip.
CCl4, on the other hand, relies on van der Waals forces, weaker bonds that are like gentle nudges.
When you mix CCl4 and water, the hydrogen bonds in water are much stronger than the van der Waals forces holding CCl4 together. These strong water bonds refuse to break apart to make room for CCl4, leading to immiscibility, a fancy word for “not mixing.”
The Visual Proof
If you were to pour CCl4 into a glass of water, you’d see two distinct layers. CCl4, being denser than water, would sink to the bottom. The two liquids would remain separate, a testament to their opposing personalities.
CCl4: Not Just a Chemistry Mystery
CCl4 is a fascinating molecule with a rich history. It was once a popular solvent and refrigerant, but its use has been greatly restricted due to its toxicity and environmental impact.
Here’s a quick rundown of its characteristics:
Colorless Liquid: It’s a clear liquid at room temperature.
Sweet Smell: But don’t be fooled by its pleasant aroma! It’s highly toxic.
Heavy: It’s denser than water, meaning it will sink.
Nonflammable: A relief, but it can release toxic fumes when heated.
Toxic and Carcinogenic: This is why its use is highly controlled.
FAQs
Now, let’s address some common questions you might have about CCl4.
1. What Happens If I Accidentally Get CCl4 On My Skin?
Run, don’t walk, to the sink! Wash the area thoroughly with soap and water. If you suspect ingestion or inhalation, get medical attention immediately.
2. Is CCl4 Used in Any Products Today?
While its use has been greatly reduced, you might find CCl4 in some older products like:
Fire Extinguishers: Some older fire extinguishers still use CCl4.
Cleaning Products: Some cleaning products like degreasers might contain CCl4.
3. Is There a Safe Alternative to CCl4?
Yes! There are plenty of safer alternatives to CCl4, such as:
Acetone: A common solvent often used in nail polish remover.
Ethanol: A type of alcohol often used in beverages and as a solvent.
Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK): A solvent often used in paints and coatings.
4. Why is CCl4 so Dangerous?
CCl4 can harm your liver, kidneys, and nervous system, leading to long-term health problems. It’s also been linked to cancer, making it a very serious threat.
Key Takeaways
CCl4 and water are like oil and water – they don’t mix!
* The “like dissolves like” rule explains this: polar molecules like water mix with other polar molecules, while nonpolar molecules like CCl4 prefer to hang out with other nonpolar molecules.
CCl4 is a toxic and potentially carcinogenic substance, so it’s crucial to handle it with extreme care and use safe alternatives whenever possible.
Hopefully, this explanation has cleared up any confusion about CCl4’s solubility in water. Remember, if you ever have any questions about chemicals, always consult with a trusted source like a chemist or your local poison control center. Stay safe, and happy experimenting!
Is CCl4 (Carbon tetrachloride) Soluble or Insoluble in
The question is whether CCl4 (Carbon tetrachloride) soluble or insoluble in water? The answer is that CCl4 is not soluble in water. YouTube
Solubility in carbon tetrachloride – Chemistry Stack Exchange
A question about which substances are more soluble in CCl4, a non-polar solvent. The answers suggest using the like dissolves like principle and provide Chemistry Stack Exchange
Why CCl4 does not dissolve in water while SiCl4 does?
A question and answer site for chemistry enthusiasts. Learn why CCl4 does not dissolve in water while SiCl4 does, and how d-orbitals are related to the solubility. Chemistry Stack Exchange
The solubility of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in water at 25 °C i …
Learn why chloroform (CHCl3) is almost ten times more soluble in water than carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) at 25 °C. Watch a video solution and see the solubility rules and Pearson
Carbon Tetrachloride | CCl4 | CID 5943 – PubChem
Carbon Tetrachloride | CCl4 | CID 5943 – structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, PubChem
Carbon Tetrachloride – NIST Chemistry WebBook
Quantity Value Units Method Reference Comment; Δ f H° liquid-128.1 ± 2.5: kJ/mol: Review: Manion, 2002: adopted combustion calorimetry data of Hu and Sinke, 1969 with NIST Chemistry WebBook
Carbon Tetrachloride – Properties, Uses,
Learn about the structure, properties, applications, and health hazards of carbon tetrachloride, an organic compound with the formula CCl4. Find out why CCl4 is not very soluble in water and how it is decomposed by steam. BYJU’S
The solubility of carbon tetrachloride in water and seawater
The solubility of CCl 4 in water and seawater has been measured for temperatures ranging from ∼0 to 40°C, and the results fit to equations used in previous ScienceDirect
Solubility Demonstration I — Like Dissolves Like
Both funnels contain CCl 4 and water. The CCl 4, having a greater density, is the lower layer I 2 crystals are added to the first funnel. KMnO 4 crystals are added to the second funnel. Chemistry LibreTexts
Is Ccl4 (Carbon Tetrachloride) Soluble Or Insoluble In Water?
Solubility Of Organic Compounds
Solubility Of Iodine In Water And Carbon Tetrachloride
How To Determine If Ionic Compound Is Soluble Or Insoluble In Water Examples, Solubility Rules
Which Molecule Would You Expect To Be More Soluble In Water, Ccl4 Or Ch2Cl2?
Which Molecule Would You Expect To Be More Soluble In Water, Ccl4 Or Ch2Cl2?
Polarity Water And Carbon Tetrachloride
\\( \\Mathrm{Ccl}_{4} \\) Is Insoluble In Water Because: (A) \\( \\Mathrm{Ccl}_{4} \\) Is Non-Polar An…
Link to this article: is ccl4 soluble in water.
See more articles in the same category here: https://bmxracingthailand.com/what
