Is propanoic acid polar or non-polar?
Let’s break down why these bonds make propanoic acid polar.
Polar Bonds: A polar bond occurs when two atoms with different electronegativities share electrons. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. Oxygen is more electronegative than both carbon and hydrogen. This means that in the C=O and O-H bonds, the electrons spend more time closer to the oxygen atom, creating a partial negative charge (δ-) on the oxygen and a partial positive charge (δ+) on the carbon and hydrogen.
Molecular Polarity: The polarity of a molecule depends on the arrangement of its polar bonds and its overall shape. Propanoic acid has a bent shape due to the presence of the O-H bond and the carbonyl group. This bent shape means the polar bonds don’t cancel each other out, resulting in an overall polar molecule.
Impact of Polarity: The polarity of propanoic acid makes it soluble in water, a polar solvent. This is because polar molecules are attracted to each other through dipole-dipole interactions.
Is propanoic acid soluble in water?
Is propanoic acid soluble in water?
Yes, propionic acid is soluble in water. This is because it can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Here’s why:
Hydrogen Bonding: Propionic acid has a carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end. The hydrogen atom in this group is slightly positive, while the oxygen atom is slightly negative. Water molecules also have a similar positive and negative charge distribution. These opposite charges attract, forming hydrogen bonds between propionic acid and water molecules.
Polarity: Propionic acid is a polar molecule. This means it has a positive and a negative end, just like water. Polar molecules tend to dissolve in other polar molecules.
Solubility: The ability of propionic acid to form hydrogen bonds with water and its polar nature make it soluble in water.
You can often find propionic acid in foods as a preservative. It’s also a common ingredient in some types of animal feed.
What type of bond is propanoic acid?
Let’s break down why. Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a nonmetal. In the case of propanoic acid, the sodium (Na) is a metal and the propanoate group (C₂H₅COO⁻) is a nonmetal. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, occur between two nonmetals. The sodium ion (Na⁺) and the propanoate ion (C₂H₅COO⁻) are attracted to each other because of their opposite charges. This attraction is what forms the ionic bond.
To further illustrate, consider the structure of propanoic acid (CH₃CH₂COOH). The hydrogen atom in the carboxyl group (COOH) is acidic. This means it can easily detach as a proton (H⁺), leaving behind a negatively charged propanoate ion (C₂H₅COO⁻). When sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to propanoic acid, the sodium ion (Na⁺) from NaOH will combine with the propanoate ion (C₂H₅COO⁻) to form sodium propanoate (C₂H₅COONa). The sodium propanoate is an ionic compound because it consists of a metal cation (Na⁺) and a nonmetal anion (C₂H₅COO⁻).
What type of molecule is propanoic acid?
Propanoic acid is a clear, oily liquid with a pungent odor. It is found naturally in some foods, such as cheese and bread. It is also used as a food preservative and in the production of plastics and pharmaceuticals.
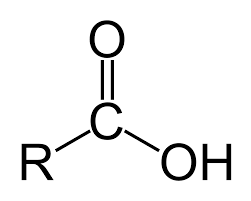
Carboxylic acids are a large and important class of organic compounds. They are characterized by the presence of the carboxyl group, which is a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group. The carboxyl group is responsible for the acidic properties of carboxylic acids.
The carboxyl group can donate a proton (H+) to a base, forming a carboxylate anion (RCOO-). This makes carboxylic acids weak acids. The acidity of a carboxylic acid is determined by the nature of the R group.
The R group in carboxylic acids can be a variety of different groups, including alkyl, aryl, or other functional groups. The nature of the R group can affect the acidity of the carboxylic acid. For example, carboxylic acids with electron-withdrawing groups are more acidic than those with electron-donating groups.
Carboxylic acids are important in many biological and industrial processes. They are found in many natural products, such as fats, oils, and waxes. They are also used in the production of polymers, plastics, and pharmaceuticals.
Is carboxylic acid polar or nonpolar?
Let’s break down why this makes carboxylic acids polar:
Polarity: A molecule is considered polar when it has an uneven distribution of electron density, resulting in a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other. This uneven distribution is often due to the presence of electronegative atoms like oxygen.
Hydrogen Bonding: Hydrogen bonding is a strong type of intermolecular force that occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom like oxygen. In carboxylic acids, the oxygen in the hydroxyl group and the oxygen in the carbonyl group are both highly electronegative, making them capable of forming hydrogen bonds with other molecules, including water.
Carboxylic Acids and Water: Because of their polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds, carboxylic acids are generally soluble in water. This is why they’re often used in a variety of applications, including pharmaceuticals, food additives, and industrial chemicals.
Let’s put it simply: Imagine a tiny magnet. One end is positive, and the other end is negative. Carboxylic acids are like these tiny magnets, attracting water molecules because of their similar polarity. This attraction helps them dissolve in water.
Think of it this way: Water is like a big, friendly party where everyone’s invited. Carboxylic acids are like the guests who can easily join in the fun because they’re also friendly and have similar personalities (polarity).
Is Pentanoic acid nonpolar?
Let’s break down why pentanoic acid is not nonpolar. The carboxyl group (-COOH) is a functional group that contains a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH). The carbonyl group is polar because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, meaning it attracts electrons more strongly. This creates a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the carbon atom. The hydroxyl group is also polar due to the difference in electronegativity between oxygen and hydrogen. This creates a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom.
The combination of the polar carbonyl and hydroxyl groups in the carboxyl group makes the entire pentanoic acid molecule polar. This means that pentanoic acid can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, which helps it dissolve in water.
Here’s a simple way to think about it:
Polar molecules are like magnets. They have a positive end and a negative end, allowing them to attract each other and other polar molecules.
Nonpolar molecules are like unmagnetized objects. They don’t have a positive or negative end, so they can’t attract each other or other polar molecules.
Since pentanoic acid has a polar carboxyl group, it can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. These hydrogen bonds are what allow pentanoic acid to dissolve in water.
How does propanoic acid react with water?
Propanoic acid, also known as propionic acid, acts as a weak acid when it’s in water. This means it doesn’t completely break apart into its ions. Instead, it reaches a balance between its original form and its ionized form.
Here’s how it works:
Propanoic acid (CH3CH2COOH) donates a hydrogen ion (H+) to water, forming hydronium ions (H3O+) and propionate ions (CH3CH2COO-). This process is called ionization and is represented by the following equilibrium reaction:
CH3CH2COOH (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ CH3CH2COO- (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
The equilibrium favors the reactants, meaning that most of the propanoic acid stays in its original form. However, there are still some propionate ions and hydronium ions present, which is why propanoic acid is considered acidic.
Let’s go a little deeper:
* The strength of an acid is measured by its acid dissociation constant (Ka). A higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid, meaning it ionizes more readily in water. Propanoic acid has a relatively low Ka value, which is why it’s considered a weak acid.
* The pH of a solution of propanoic acid will be less than 7, because of the presence of hydronium ions. The lower the pH, the more acidic the solution.
The reaction of propanoic acid with NaOH:
When propanoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a neutralization reaction occurs. This reaction produces sodium propionate (CH3CH2COONa), a salt, and water (H2O). The reaction can be represented as:
CH3CH2COOH (aq) + NaOH (aq) → CH3CH2COONa (aq) + H2O (l)
The propionate ion formed in this reaction is the conjugate base of propanoic acid. It is a weak base, meaning it doesn’t readily accept hydrogen ions. The neutralization reaction between propanoic acid and sodium hydroxide results in a solution with a pH closer to 7.
In summary, propanoic acid reacts with water to form propionate ions and hydronium ions, but the equilibrium favors the reactants, making it a weak acid. This means it doesn’t fully ionize in water and has a relatively low Ka value. However, the presence of hydronium ions in solution results in an acidic pH.
See more here: Is Propanoic Acid Soluble In Water? | Propanoic Acid Polar Or Nonpolar
Why is propionic acid a compound?
Propionic acid is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It’s found naturally in some foods, like Swiss cheese, and is also produced industrially. It’s important to understand why propionic acid is a compound, and that’s because it’s made up of different elements. The molecular formula of propionic acid is CH3CH2COOH. This means that each molecule of propionic acid contains three carbon atoms, five hydrogen atoms, two oxygen atoms. These atoms are chemically bonded together, forming a single, unique molecule. This combination of different elements makes propionic acid a compound, and it’s one of the simplest organic acids.
You might be wondering how propionic acid is linked to fats. Well, it’s the smallest acid that can be made from fatty acids. Fatty acids are long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms that are found in fats and oils. When these long chains are broken down, they can be converted into propionic acid. This process happens naturally in the bodies of animals and humans, and it’s also used to produce propionic acid industrially.
So, there you have it! Propionic acid is a compound because it’s made up of different elements bonded together in a specific way. It’s a key ingredient in many processes, from the production of cheese to the way our bodies break down fats.
Is propionic acid miscible with water?
Propionic acid is miscible with water, meaning it can dissolve completely in water. This is because of the polar nature of both the acid and water molecules. The carboxylic acid group in propionic acid (COOH) can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, leading to good solubility.
However, we can remove the acid from water by adding salt (such as sodium chloride). This is called salting out. Salts disrupt the hydrogen bonds between the propionic acid and water molecules, making the acid less soluble and causing it to separate from the water solution.
The process of salting out is based on the concept of solubility and polarity. When salt is added to a solution of propionic acid in water, the salt ions compete with the propionic acid molecules for the water molecules. Since salt ions have a stronger attraction to water molecules due to their higher charge density, the propionic acid molecules are forced to aggregate and separate from the water solution. This leads to the precipitation or separation of propionic acid from the solution.
Think of it like this: Imagine propionic acid and water molecules holding hands in a friendly dance. When you add salt, the salt ions swoop in and grab the water molecules, forcing the propionic acid to let go and fall out of the dance.
Propionic acid is similar to acetic acid and formic acid. These acids also form hydrogen-bonded pairs in both the liquid and vapor phases. They all display the typical properties of carboxylic acids, meaning they can form amide, ester, anhydride, and chloride derivatives.
Is acetic acid polar or nonpolar?
We know that water is a polar molecule. Acetic acid is also polar enough to dissolve in water. But, as you increase the number of carbons in the R group of a carboxylic acid (the part of the molecule that’s not the carboxyl group), the molecule becomes more nonpolar. This is because carbons and hydrogens form nonpolar bonds.
The more nonpolar a molecule becomes, the less soluble it is in water. This is because polar molecules like water tend to dissolve other polar molecules, and nonpolar molecules like to dissolve other nonpolar molecules. Think of it like oil and water – they don’t mix because they have different polarities.
Let’s break down why acetic acid is polar and how its polarity changes as we add more carbons.
Acetic acid has a carboxyl group (-COOH). This group contains an oxygen atom that’s double-bonded to a carbon atom and also single-bonded to an OH group. This arrangement makes the carboxyl group very polar. The oxygen atom is more electronegative than the carbon and hydrogen atoms, meaning it attracts electrons more strongly. This creates a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Now, consider what happens when we add more carbons to the R group of acetic acid. These carbons are bonded to hydrogens, forming nonpolarC-H bonds. As we add more of these nonpolar bonds, the molecule becomes more nonpolar overall. This is because the polar nature of the carboxyl group is diluted by the increasing number of nonpolarC-H bonds.
So, while acetic acid itself is polar enough to dissolve in water, as we increase the size of the R group and add more carbons, the molecule becomes less polar and less soluble in water.
See more new information: bmxracingthailand.com
Propanoic Acid: Polar Or Nonpolar? Understanding The Molecule’S Nature
Understanding Polarity
Before we tackle propanoic acid, let’s understand what polarity means. Think of a molecule as a tiny magnet with a positive end and a negative end. If those ends are unevenly distributed, creating a slight positive and negative charge, we call that molecule polar. But if the charge is evenly spread, it’s nonpolar.
The Structure of Propanoic Acid
Propanoic acid (CH3CH2COOH) has a few key features:
Carbon Chain: It has a hydrocarbon chain (made of carbon and hydrogen), which is usually nonpolar.
Carboxylic Acid Group: The COOH group is where the magic happens. This group has a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (OH).
The Verdict: Propanoic Acid is Polar
Here’s the breakdown:
* The carbonyl group has a polar bond due to the difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen.
* The hydroxyl group is also polar due to the difference in electronegativity between oxygen and hydrogen.
These polar bonds create a dipole moment, giving the entire propanoic acid molecule a net dipole. Therefore, propanoic acid is polar.
Why Polarity Matters
Polarity is important because it influences how molecules interact with each other and with other substances.
Solubility: Polar molecules tend to dissolve in polar solvents like water, while nonpolar molecules dissolve in nonpolar solvents like oil.
Boiling Point:Polar molecules have higher boiling points than nonpolar molecules. This is because polar molecules form stronger intermolecular forces, which require more energy to overcome.
Reactivity:Polar molecules are more likely to react with other polar molecules, while nonpolar molecules are more likely to react with other nonpolar molecules.
Propanoic Acid and its Uses
Propanoic acid is used in various industries:
Food Preservation: It’s a natural antimicrobial, commonly used in bread, cheese, and other foods to inhibit mold and bacteria growth.
Animal Feed: It’s added to animal feed to promote growth and improve digestion.
Manufacturing: It’s used to make various chemicals, including plastics and pharmaceuticals.
FAQs
Q: Can propanoic acid be found naturally?
A: Yes, propanoic acid is naturally found in some cheeses, bread, and even in the human body.
Q: Is propanoic acid safe to eat?
A: Yes, propanoic acid is generally recognized as safe by the FDA and is commonly used in food as a preservative.
Q: What’s the difference between propanoic acid and propionic acid?
A: These are two names for the same compound! You might see both names used interchangeably.
Q: How is propanoic acid produced?
A: Propanoic acid is produced by the fermentation of sugars by certain bacteria. It can also be made synthetically.
Q: Are there any environmental concerns related to propanoic acid?
A: Propanoic acid is considered biodegradable and doesn’t pose significant environmental risks at normal concentrations.
Let me know if you have more questions about propanoic acid or polarity!
Propionic Acid | CH3CH2COOH | CID 1032 – PubChem
Propionic Acid | CH3CH2COOH or C3H6O2 | CID 1032 – structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. PubChem
Propanoic acid – NIST Chemistry WebBook
Molecular weight: 74.0785. IUPAC Standard InChI:InChI=1S/C3H6O2/c1-2-3 (4)5/h2H2,1H3, (H,4,5) Copy. IUPAC Standard InChIKey:XBDQKXXYIPTUBI NIST Chemistry WebBook
Propionic acid | C3H6O2 | ChemSpider
Structure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for: Propionic acid, 79-09-4, C3:0. ChemSpider
Propanoic acid – NIST Chemistry WebBook
Molecular weight: 74.0785. IUPAC Standard InChI:InChI=1S/C3H6O2/c1-2-3 (4)5/h2H2,1H3, (H,4,5) Copy. IUPAC Standard InChIKey:XBDQKXXYIPTUBI NIST Chemistry WebBook
Molecular polarity (video) | VSEPR | Khan Academy
In a polar molecule, electron density is unevenly distributed throughout the molecule, resulting in regions of partial negative charge and regions of partial positive charge. Molecular polarity depends on both individual bond polarities and molecular Khan Academy
Propanoic acid – NIST Chemistry WebBook
Molecular weight: 74.0785. IUPAC Standard InChI:InChI=1S/C3H6O2/c1-2-3 (4)5/h2H2,1H3, (H,4,5) Copy. IUPAC Standard InChIKey:XBDQKXXYIPTUBI NIST Chemistry WebBook
Carboxylic acid nomenclature and properties – Khan Academy
Acetic acid is soluble in water. Water is a polar molecule. Acetic acid is polar enough to dissolve in water. However, as you increase the number of carbons in your R group, as you increase the number of carbons, you get more carbons and Khan Academy
2: Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar …
2.E: Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules (Exercises) 2: Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Chemistry LibreTexts
4.12: Shapes and Properties- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
To determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar, it is frequently useful to look at Lewis structures. Nonpolar compounds will be symmetric, meaning all of the Chemistry LibreTexts
Identifying Amino Acid Side Chains As Polar, Non-Polar Or Charged – Real Chemistry
World Strongest Acid On Skin #Shorts
Amino Acids: Polar Vs Non-Polar, Acidic, Basic, And Neutral
Polar And Nonpolar Molecules: How To Tell If A Molecule Is Polar Or Nonpolar
Polar And Nonpolar Molecules
Sulphuric Acid #Shorts
Is Ch3Cooh Polar Or Nonpolar? (Acetic Acid)
Polar \U0026 Non-Polar Molecules: Crash Course Chemistry #23
Link to this article: propanoic acid polar or nonpolar.
See more articles in the same category here: https://bmxracingthailand.com/what
