When ethyl bromide is treated with sodium ethoxide, the major product is?
Let’s break down the process:
Williamson Ether Synthesis: The reaction between an alkyl halide (like ethyl bromide) and an alkoxide ion (like sodium ethoxide) produces an ether. This reaction is named after Alexander Williamson, who discovered it in 1850.
SN2 Mechanism: In this type of reaction, the nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom from the backside, resulting in a one-step process where the leaving group departs simultaneously. In this case, the ethoxide ion attacks the ethyl bromide, displacing the bromide ion and forming diethyl ether.
Hydrogenation: This process involves the addition of hydrogen gas (H2) to a molecule, typically in the presence of a catalyst. In this case, diethyl ether is hydrogenated to produce butane. The hydrogen atoms are added across the double bond of the ether, resulting in a saturated hydrocarbon.
You can think of hydrogenation as a way to “reduce” the molecule, adding hydrogen atoms and removing double bonds. The reaction usually occurs under high pressure and temperature, with a metal catalyst like nickel, palladium, or platinum facilitating the process.
So, in summary, the reaction of ethyl bromide with sodium ethoxide produces diethyl ether, which is then hydrogenated to form butane. This reaction exemplifies the Williamson ether synthesis and showcases the versatility of organic reactions, allowing for the creation of various functional groups and molecules.
What happens when ethyl chloride reacts with sodium ethoxide?
Assertion: Ethyl chloride reacts with sodium ethoxide to form diethyl ether. Here the ethoxide ion acts as a strong base.
Reason: C2H5OH (ethanol) is a weak acid.
Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Let’s dive a little deeper. Sodium ethoxide (NaOCH2CH3) is a strong base because it readily donates its negatively charged ethoxide ion (OCH2CH3-). The ethoxide ion is a powerful nucleophile, meaning it’s attracted to positively charged centers. In ethyl chloride (CH3CH2Cl), the carbon atom bonded to the chlorine atom carries a slight positive charge. This makes it a prime target for the nucleophilic attack by the ethoxide ion.
During the reaction, the ethoxide ion displaces the chlorine atom from the ethyl chloride molecule. This results in the formation of diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3) and sodium chloride (NaCl).
Here’s a simplified representation of the reaction:
CH3CH2Cl + NaOCH2CH3 → CH3CH2OCH2CH3 + NaCl
Why is the reason relevant? The fact that ethanol is a weak acid is crucial to understanding the reaction’s mechanism. Since ethanol is a weak acid, its conjugate base (the ethoxide ion) is a strong base. This is why the ethoxide ion is so reactive and can easily displace the chlorine atom from ethyl chloride.
This reaction highlights the power of nucleophilic substitution reactions. These reactions are fundamental to organic chemistry and are essential in the synthesis of various compounds, including ethers, esters, and amides.
What happens when sodium ethoxide reacts with ethanol?
You might be wondering what happens when sodium ethoxide reacts with ethanol. Well, it’s a pretty straightforward reaction, and here’s the breakdown:
Sodium reacts with ethanol to produce sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas. The reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat, and you’ll see bubbles of hydrogen gas forming in the solution. This reaction is represented by the following chemical equation:
2 CH3CH2OH (l) Ethanol + 2 Na (s) Sodium → 2 CH3CH2ONa (l) Sodium ethoxide + H2 (g) Hydrogen
Let’s break down what’s happening here:
Sodium is a highly reactive metal, and when it comes into contact with ethanol, it readily donates an electron to the ethanol molecule.
* This electron transfer forms a sodium ethoxide ion (CH3CH2O-) and a hydrogen ion (H+).
* The hydrogen ions then combine to form hydrogen gas (H2), which is what you see as the bubbles in the solution.
Sodium ethoxide is a strong base, and it’s often used as a reagent in organic chemistry. Its ability to act as a base comes from the negatively charged oxygen atom in the ethoxide ion, which is readily available to accept a proton (H+).
Diving Deeper
The reaction of sodium with ethanol is an example of a single displacement reaction. This is a type of reaction where one element replaces another in a compound. In this case, sodium replaces the hydrogen in ethanol, forming sodium ethoxide and releasing hydrogen gas.
The reaction is also a redox reaction, meaning that there’s a transfer of electrons between the reactants. Sodium loses an electron to become sodium ethoxide, while hydrogen gains an electron to form hydrogen gas.
Sodium ethoxide is a valuable reagent in organic chemistry, particularly in reactions involving nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions. It’s also used in the production of biodiesel and other organic compounds.
Understanding the reaction between sodium and ethanol helps us understand the fundamental principles of chemistry, including single displacement reactions, redox reactions, and the role of strong bases in organic chemistry.
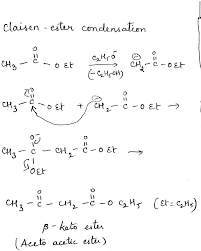
What is the reaction of sodium ethoxide and ethyl acetate?
The reaction of ethyl acetate with sodium ethoxide gives acetoacetic ester. This reaction is a classic example of a Claisen condensation, a crucial reaction in organic chemistry for forming β-keto esters.
Let’s dive a bit deeper into what’s happening here. Sodium ethoxide acts as a strong base, and it’s this basicity that drives the Claisen condensation. When sodium ethoxide encounters ethyl acetate, it pulls off a proton (H+) from the alpha-carbon of ethyl acetate. This alpha-carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group. This deprotonation creates an enolate ion, which is a very reactive species.
The enolate ion then attacks another molecule of ethyl acetate at its carbonyl group. This attack leads to the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond and the creation of acetoacetic ester. The reaction also generates ethanol as a byproduct.
Here’s a simplified breakdown:
Step 1: Sodium ethoxide deprotonates ethyl acetate, forming an enolate ion.
Step 2: The enolate ion attacks another molecule of ethyl acetate, forming a new carbon-carbon bond and acetoacetic ester.
The Claisen condensation is a powerful tool in organic synthesis, and it’s used to build complex molecules starting from simpler ones. Acetoacetic ester itself is a versatile building block for various organic compounds.
What happens when ethylene oxide reacts with sodium ethoxide?
Let’s break down what’s happening at the molecular level. Sodium ethoxide is a strong base, and its negative charge resides on the oxygen atom. This negatively charged oxygen is attracted to the slightly positive carbon atom in the ethylene oxide ring. The sodium ethoxide acts as a nucleophile, attacking the ethylene oxide ring and opening it up. The result is the formation of a new carbon-oxygen bond and a new molecule, 2-ethoxyethanol.
The reaction mechanism is quite straightforward. The sodium ethoxide attacks the ethylene oxide ring, breaking the ring and forming a new C-O bond. The product, 2-ethoxyethanol, is a versatile compound used in various applications, including as a solvent and in the production of other chemicals.
This reaction showcases the power of nucleophilic attack in organic chemistry, where the attack of an electron-rich species (the nucleophile) on an electron-deficient species (the electrophile) leads to the formation of new bonds and, in this case, a new, useful compound.
What is the reaction of sodium ethoxide to ethyl methyl ether?
The reaction is initiated by the attack of the ethoxide ion on the methyl group of ethyl methyl ether. This results in the displacement of the ethoxy group, which leaves as an anion.
The product of the reaction is sodium ethoxide and methyl ethyl ether.
Let’s break down how the SN2 reaction happens:
1. Nucleophile attack: The ethoxide ion (from sodium ethoxide) is a strong nucleophile. It attacks the methyl carbon in ethyl methyl ether, forming a bond between the oxygen atom of the ethoxide ion and the carbon atom of the methyl group.
2. Leaving group departure: As the ethoxide ion attacks, the ethoxy group (OCH2CH3) is forced to leave. It takes the pair of electrons that were bonding it to the carbon atom.
3. Product formation: The result is a new ether, methyl ethyl ether, and the ethoxide ion has been replaced by the methyl group.
Here’s an analogy: Imagine you have a Lego structure with a red brick attached. You want to replace the red brick with a blue brick. You can’t just pull off the red brick because it’s held in place. So, you use a blue brick as a nucleophile to push the red brick out of the way. This creates a new structure with the blue brick in place.
It’s important to note that this reaction only occurs under specific conditions. It requires a strong base like sodium ethoxide, and the presence of a good leaving group like the ethoxy group.
The SN2 reaction is a common reaction in organic chemistry and is used to synthesize a variety of compounds, including ethers. It’s a versatile reaction that can be used to create new molecules with specific properties.
How does ethyl bromide react with sodium ethoxide?
When ethyl bromide is heated with sodium ethoxide, diethyl ether is formed. This reaction is a classic example of a Williamson ether synthesis.
Here’s what happens:
Sodium ethoxide (NaOCH2CH3) is a strong base, and it attacks the ethyl bromide (CH3CH2Br) molecule.
* The ethoxide ion (OCH2CH3-) replaces the bromine atom, resulting in the formation of diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3).
This reaction is often used to prepare symmetrical ethers, where both alkyl groups are the same. For example, diethyl ether is a symmetrical ether.
Now, let’s dive a bit deeper into the Williamson ether synthesis:
The Williamson ether synthesis is a versatile reaction that allows us to create various ethers. It involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion (RO-) with an alkyl halide (R’X). This reaction works well for both primary and secondary alkyl halides.
The beauty of this reaction lies in its ability to create both symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. In the case of symmetrical ethers, we use the same alkyl halide and alkoxide. For example, reacting methyl bromide with sodium methoxide produces dimethyl ether.
Unsymmetrical ethers, on the other hand, are created when the alkyl halide and alkoxide have different alkyl groups. For example, reacting methyl bromide with sodium ethoxide yields ethyl methyl ether.
Remember, the Williamson ether synthesis is a powerful tool for organic chemists, providing a reliable route to synthesizing a wide range of ethers.
See more here: When Ethyl Bromide Is Treated With Sodium Ethoxide, The Major Product Is? | Reaction Of Sodium Ethoxide With Ethyl Bromide
See more new information: bmxracingthailand.com
Reaction Of Sodium Ethoxide With Ethyl Bromide | What Will Happen If Ethyl Bromide Reacts With Sodium Ethoxide?
Hey there, chemistry enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to dive into the fascinating world of organic reactions, specifically the reaction of sodium ethoxide with ethyl bromide. This reaction is a classic example of Williamson ether synthesis, and it’s a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry.
Sodium ethoxide (C2H5ONa), a strong base, reacts with ethyl bromide (C2H5Br), a primary alkyl halide, to produce diethyl ether (C2H5OC2H5) and sodium bromide (NaBr). This reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where the ethoxide ion acts as a nucleophile, attacking the electrophilic carbon atom in ethyl bromide.
Understanding the Mechanism
Let’s break down the reaction mechanism step-by-step:
1. Formation of the Ethoxide Ion: Sodium ethoxide dissolves in ethanol to form ethoxide ions (C2H5O-) and sodium ions (Na+).
“`
C2H5ONa (s) + C2H5OH (l) → C2H5O- (aq) + Na+ (aq) + C2H5OH (l)
“`
2. Nucleophilic Attack: The ethoxide ion, being a strong nucleophile, attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in ethyl bromide. The carbon-bromine bond breaks, leading to the formation of a new carbon-oxygen bond.
“`
C2H5O- + C2H5Br → C2H5OC2H5 + Br-
“`
3. Formation of Diethyl Ether and Sodium Bromide: The reaction produces diethyl ether and sodium bromide. The sodium bromide is a spectator ion, meaning it doesn’t participate in the reaction.
“`
C2H5OC2H5 + NaBr → C2H5OC2H5 (l) + NaBr (aq)
“`
Factors Affecting the Reaction
Several factors influence the success of the Williamson ether synthesis. These include:
Nature of the Alkyl Halide: Primary alkyl halides react faster than secondary alkyl halides, which in turn react faster than tertiary alkyl halides. This is because the steric hindrance surrounding the electrophilic carbon atom increases with the increasing branching of the alkyl chain.
Strength of the Base: A stronger base like sodium ethoxide is more likely to facilitate the reaction.
Solvent: The choice of solvent is crucial. Polar aprotic solvents like dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or tetrahydrofuran (THF) are preferred as they dissolve the reactants and stabilize the transition state.
Temperature: Higher temperatures generally lead to faster reactions.
Applications of Williamson Ether Synthesis
Williamson ether synthesis has wide applications in organic chemistry:
Synthesis of Ethers: This reaction is the most important method for preparing symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
Synthesis of Cyclic Ethers: The reaction can be used to synthesize cyclic ethers, which are important intermediates in organic synthesis.
Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals: Many pharmaceutical compounds contain ether functionalities, and Williamson ether synthesis is a key step in their synthesis.
FAQs
Q: Why is sodium ethoxide used as a base in Williamson ether synthesis?
A: Sodium ethoxide is a strong base that can deprotonate ethanol to generate the ethoxide ion. This ethoxide ion is a strong nucleophile and readily attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in the alkyl halide.
Q: What are the advantages of Williamson ether synthesis?
A: Williamson ether synthesis is a versatile and efficient method for synthesizing ethers. It offers excellent yields and allows for the preparation of a wide range of ethers, both symmetrical and unsymmetrical.
Q: What are some limitations of Williamson ether synthesis?
A: Williamson ether synthesis can be limited by the reactivity of the alkyl halide. Tertiary alkyl halides often undergo elimination reactions rather than nucleophilic substitution.
Q: What other methods can be used to synthesize ethers besides Williamson ether synthesis?
A: Other methods for synthesizing ethers include:
Alkoxymercuration-demercuration: This method involves the reaction of an alkene with an alcohol in the presence of mercury(II) acetate, followed by reduction with sodium borohydride.
Acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols: This method involves the dehydration of two molecules of alcohol in the presence of a strong acid catalyst.
Q: How can I improve the yield of Williamson ether synthesis?
A: To improve the yield of Williamson ether synthesis, you can:
* Use a strong base like sodium ethoxide.
* Use a polar aprotic solvent like DMSO or THF.
* Increase the reaction temperature.
* Remove any side products as they form to drive the equilibrium towards product formation.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the reaction of sodium ethoxide with ethyl bromide, its mechanism, factors affecting it, and its applications. Feel free to ask any further questions in the comments section below!
What Happens When ? (A) Ethyl Bromide Reacts With Sodium Ethoxide. (B) Ethyl Alcohol Is Heated With
Action Of Sodium Ethoxide With Ethyl Bromide Williamson Synthesis
Formation Of Ethoxy Ether. By Reaction Of Ethyl Bromide And Sodium Ethoxide
Ethyl Iodide Reacts With Sodium Ethoxide To Form
Heating Together Of Sodium Ethoxide And Ethyl Iodide Will Give:
The Reaction Of Ethyl Iodide With Sodium Ethoxide Is (1) An Electrophilic Substitution Reaction (…
When Ethylbromide And Propyl Bromide Are Allowed To Reacts With Sodium In Ether, They Form
The Reaction Of Sodium Ethoxide With Ethyl Iodide To Form Diethyl E…
Reaction Between Ethyl Bromide And Ethoxide.
Name The Products When Ethyl Bromide And Methyl Bromide Are Treated With Sodium Metal.
Link to this article: reaction of sodium ethoxide with ethyl bromide.
See more articles in the same category here: bmxracingthailand.com/what
