What is not part of the endomembrane system?
Let’s break down why mitochondria are excluded. The endomembrane system is characterized by its interconnectedness. It’s like a series of rooms in a house, each with its specific function, but all connected by doors. These “rooms” include the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi complex, lysosomes, and vacuoles. Each of these compartments plays a specific role in the cell’s overall function. The ER is like the kitchen, where proteins and lipids are synthesized. The Golgi complex acts as the packaging and shipping department, modifying and sorting newly made molecules. Lysosomes are the recycling center, breaking down worn-out cellular components. Vacuoles are the storage tanks, holding water and other important molecules.
Mitochondria, on the other hand, are like a separate house entirely. They are self-contained organelles with their own DNA and ribosomes, and they have a unique structure with two membranes. Their primary function is energy production, generating ATP through cellular respiration. This distinct function and structure distinguish them from the components of the endomembrane system. While they work in cooperation with other cellular components, they don’t rely on the same interconnected network of membranes as the endomembrane system does.
Which structures are part of the endomembrane system?
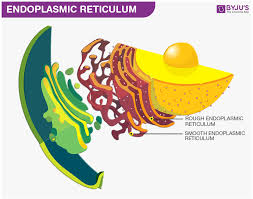
Think of the ER as a vast network of interconnected sacs and tubes. It’s like a factory floor, where proteins and lipids are manufactured, folded, and modified. The rough ER, studded with ribosomes, is the primary site of protein synthesis. The smooth ER, lacking ribosomes, plays a role in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage.
Once proteins and lipids are processed in the ER, they’re shipped to the Golgi apparatus. This organelle acts like a sorting and packaging center. It further modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids into vesicles, tiny membrane-bound sacs that act like delivery trucks.
These vesicles can then transport their cargo to various destinations within the cell. Some may even fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents outside the cell. Others might deliver their contents to lysosomes, which act like recycling centers. These organelles contain powerful enzymes that break down old or damaged cellular components.
The endomembrane system is incredibly dynamic and plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular function. By working together, these organelles ensure that proteins and lipids are produced, modified, packaged, and transported efficiently, keeping the cell healthy and functioning smoothly.
Which structure is not technically part of the endomembrane system?
Let’s break down why. The endomembrane system is characterized by its interconnectedness. The organelles within this system communicate and interact through the movement of vesicles, small membrane-bound sacs that transport molecules between them. The membranes of the endomembrane system are continuous, meaning they are connected and share a similar composition.
Mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes, while essential for cellular function, don’t fit this model. They have their own unique membranes and don’t interact directly with the endomembrane system through vesicle transport. Mitochondria are responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration. Chloroplasts, found in plant cells, carry out photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy. Peroxisomes are involved in various metabolic reactions, including detoxification and lipid breakdown.
Think of it like this: Imagine the endomembrane system is a bustling factory with different departments (organelles) working together to create and ship products (proteins and lipids). Mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes are like independent workshops, crucial to the factory’s overall function but operating independently with their own specialized equipment and processes.
What structure is not part of the endomembrane system Quizlet?
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is also a part of the endomembrane system. The smooth ER is involved in a variety of cellular functions, including the synthesis of lipids, the detoxification of drugs and poisons, and the storage of calcium ions. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of phospholipids, steroids, and other lipids. It also helps in the detoxification of harmful substances, including drugs and toxins, by modifying them into less toxic forms.
The rough ER is so named because of the ribosomes attached to its surface. These ribosomes are responsible for the synthesis of proteins, which are then transported to other parts of the cell. The rough ER also plays a role in the modification and packaging of proteins.
The endomembrane system helps to organize the cell’s internal environment, and it is essential for the proper functioning of eukaryotic cells.
What organelle is not in the Endomembrane?
Let’s break down why the mitochondria stands apart. The endomembrane system is all about interconnectedness. These organelles communicate with each other through the movement of small vesicles, which are like tiny sacs that carry materials from one part of the cell to another. The ER is the starting point for many of these processes. It’s a network of interconnected membranes that act as a factory for synthesizing and modifying proteins and lipids. The Golgi complex then receives these products from the ER and further refines them, packaging them into new vesicles that can be sent to other parts of the cell or even released outside the cell. Lysosomes, meanwhile, are the recycling centers of the cell, breaking down waste products and worn-out organelles. Vacuoles, especially prominent in plant cells, are storage tanks for water, nutrients, and waste products.
The mitochondria, on the other hand, are like powerhouses within the cell. They are responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration. Unlike the other organelles in the endomembrane system, mitochondria have their own separate membranes and DNA. They are more closely related to bacteria and have a unique evolutionary origin. They’re self-sufficient, able to replicate on their own, and don’t rely on the endomembrane system for their primary function.
Which of the following is not a function of the endomembrane system?
Let’s break down why plasma isn’t a product of the endomembrane system. The endomembrane system includes components like the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles. These organelles work together in a coordinated fashion to perform a variety of essential functions:
Protein Synthesis and Modification: The ER, particularly the rough ER, is studded with ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis. The proteins synthesized on the ER can be modified, folded, and transported to other parts of the cell or exported outside the cell.
Lipid Synthesis and Modification: The smooth ER is involved in the synthesis of lipids, including steroids and phospholipids, which are important for cell membranes and other functions.
Packaging and Sorting: The Golgi apparatus further modifies and packages proteins and lipids received from the ER. It acts like a sorting center, directing these molecules to their final destinations within the cell or for secretion outside the cell.
Digestion and Recycling: Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down waste materials, cellular debris, and engulfed bacteria. They are essential for maintaining cellular health and recycling cellular components.
Storage and Transport: Vacuoles, particularly large in plant cells, serve as storage compartments for water, nutrients, and waste products. They also play a role in maintaining cell shape and turgor pressure.
While the endomembrane system is vital for many cellular processes, it does not play a role in creating plasma. Plasma, as the fluid component of blood, is produced in the bone marrow by a different process involving the differentiation and development of blood cells.
Why are peroxisomes not considered part of the endomembrane system?
Let’s dive into why peroxisomes, in particular, are distinct from the endomembrane system. While the organelles within the endomembrane system communicate and work together, peroxisomes function independently. They’re self-sufficient, with their own unique set of enzymes for specific tasks. They don’t receive proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, nor do they rely on the Golgi complex for modification. Instead, peroxisomes have their own mechanism for importing the necessary proteins for their functions.
In addition, peroxisomes have their own method of replication. They don’t bud off from existing organelles like some endomembrane components do. Instead, peroxisomes grow and then divide by fission, similar to mitochondria and chloroplasts.
So, in essence, peroxisomes are unique organelles that operate independently, with their own set of enzymes and replication strategies, making them distinct from the collaborative, interconnected network of the endomembrane system.
See more here: Which Structures Are Part Of The Endomembrane System? | Which Structure Is Not Part Of The Endomembrane System
What are the components of the endomembrane system?
The Nucleus: This is the cell’s control center, housing the DNA. The nuclear membrane is a double membrane that regulates what goes in and out of the nucleus.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Think of this as the cell’s factory. There are two types of ER:
Rough ER: This is studded with ribosomes, the protein-making machines of the cell. The rough ER helps to synthesize and modify proteins.
Smooth ER: This lacks ribosomes and plays a role in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage.
The Golgi Apparatus: Imagine this as the cell’s packaging and shipping center. The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids from the ER.
Lysosomes: These are the cell’s recycling centers. They contain enzymes that break down waste materials, old organelles, and engulfed bacteria.
Endosomes: These are membrane-bound vesicles involved in the transport of materials from the cell’s exterior to its interior.
Vesicles: These are small, membrane-bound sacs that transport substances within the cell.
The Cell Membrane: This is the outer boundary of the cell, controlling what enters and exits.
Importantly, the endomembrane system does not include the membranes of mitochondria or chloroplasts. These organelles have their own distinct membranes and are thought to have originated from ancient bacteria that were engulfed by early eukaryotic cells.
How does the endomembrane system work? The membranes of this system are constantly interacting and moving, creating a dynamic network. Vesicles bud off from one organelle and fuse with another, transporting materials throughout the cell. This interconnectedness allows the different components of the endomembrane system to work together, ensuring efficient cellular function.
Let’s delve deeper into the remarkable collaboration of these components. Imagine a protein synthesized on the rough ER. This protein will then travel through the ER lumen, undergoing modifications along the way. Next, it’s packaged into a transport vesicle and shipped to the Golgi apparatus. In the Golgi, the protein may be further modified and sorted before being packaged into a new vesicle destined for its final destination. This destination could be the cell membrane for secretion, or it could be a lysosome for degradation.
The endomembrane system, with its interconnected network of membranes and organelles, represents a remarkable symphony of cellular activity. It underscores the intricate organization and remarkable efficiency that characterize life at the cellular level.
What is the endomembrane system?
Think of it as the cell’s own internal postal service. The endomembrane system receives, processes, packages, and delivers materials throughout the cell. This intricate system ensures that proteins and lipids are correctly modified, packaged, and delivered to their designated destinations, whether it’s within the cell or outside of it. This system is vital for cellular function and is essential for the survival of eukaryotic organisms.
Here are some of the key players in the endomembrane system:
The Nuclear Envelope: This double membrane encloses the cell’s nucleus and regulates the movement of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): This network of interconnected membranes is the site of protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The ER is divided into two regions: the rough ER and the smooth ER. The rough ER is studded with ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis. The smooth ER is involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage.
The Golgi Apparatus: This organelle is responsible for processing, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids. It receives materials from the ER, modifies them further, and then packages them into vesicles for transport to other destinations.
Lysosomes: These are membrane-bound organelles that act as the cell’s recycling center. They contain enzymes that break down waste materials, worn-out organelles, and ingested materials.
Vacuoles: These are large, fluid-filled sacs that store water, nutrients, and waste products. They also help to maintain the cell’s shape and turgor pressure.
These components work together in a coordinated manner, ensuring the efficient flow of materials throughout the cell. The endomembrane system is a remarkable example of how complex cellular processes are organized and integrated.
Is the plasma membrane part of the endomembrane system?
The plasma membrane plays a crucial role in this process by interacting with other endomembrane organelles, ultimately facilitating the secretion of proteins. For example, proteins destined for secretion are synthesized on ribosomes attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The ER then processes these proteins, folding them into their correct shape and sometimes adding modifications like sugars. From the ER, the proteins move to the Golgi apparatus, where they undergo further sorting and packaging. Finally, these proteins are transported to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles, where they are released into the extracellular space.
The plasma membrane’s direct involvement in this process underscores its integral role within the endomembrane system. It’s not just a barrier separating the cell’s interior from the external environment; it’s an active participant in the cell’s internal workings.
Which part of the endomembrane system does not include mitochondria?
Now, let’s focus on the ER, as it’s a key player in the endomembrane system. The ER is a network of interconnected membranes that extends throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. There are two main types of ER: the rough ER and the smooth ER. The rough ER is studded with ribosomes, which are the sites of protein synthesis. The rough ER helps to fold and modify proteins, ensuring they are properly shaped and ready for their final destination.
The smooth ER, on the other hand, lacks ribosomes and is involved in the synthesis of lipids, steroids, and detoxification of harmful substances. It also plays a crucial role in regulating calcium levels within the cell.
Once proteins and lipids are modified in the ER, they are transported to the Golgi apparatus. This organelle acts as a sorting and packaging center, further modifying and packaging these molecules into vesicles that can then be shipped to different parts of the cell or even secreted outside the cell.
The endomembrane system is a dynamic and interconnected network that is essential for the proper functioning of eukaryotic cells. While the mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes are vital organelles, they are not part of this system. They have their own independent roles in the cell, such as energy production in the case of mitochondria, photosynthesis in chloroplasts, and detoxification of harmful substances in peroxisomes.
See more new information: bmxracingthailand.com
Which Structure Is Not Part Of The Endomembrane System?
Okay, let’s dive into the world of cells, specifically the endomembrane system. You might be thinking, “What on Earth is that?”. Well, it’s like a mini-city inside your cells, with different structures working together to keep things running smoothly.
Imagine a bustling metropolis. You’ve got your factories, your post offices, your recycling centers – all working together to keep the city going. The endomembrane system is the same, just on a microscopic level.
But here’s the thing: not every cellular structure is part of this intricate network.
Ribosomes: The Lone Wolves of the Cellular World
So, which structure is the oddball that doesn’t belong? That would be the ribosome. It’s like the independent contractor, working outside the system.
While the endomembrane system is a connected network of membranes, ribosomes are free-floating particles. Think of them like little protein-making factories, but without a fixed address. They’re often attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – a major player in the endomembrane system – but they can also hang out on their own in the cytoplasm, the fluid that fills the cell.
The Endomembrane System: A Network of Interconnected Structures
Now, let’s talk about the endomembrane system itself. This intricate network of membranes is responsible for many essential cellular functions. Here are the key players:
Nuclear Envelope: This double membrane surrounds the nucleus, the cell’s control center. Think of it as the city hall, where the blueprints for making proteins are stored.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): This is like a vast network of interconnected sacs and tubes. It’s the cell’s manufacturing plant, producing proteins and lipids (fats). There are two types of ER:
Rough ER: It’s rough because it has ribosomes attached, which are busy making proteins. Think of it as the factory floor where proteins are assembled.
Smooth ER: It’s smooth because it lacks ribosomes. Here, lipids are synthesized, and toxins are detoxified. Think of it as the factory’s clean-up crew and packaging department.
Golgi Apparatus: This structure is like the cell’s post office, processing, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for delivery to other parts of the cell or even outside the cell.
Lysosomes: These are the cell’s recycling centers. They break down worn-out cell parts, engulf invaders like bacteria, and even dispose of unwanted molecules.
Vacuoles: These are like storage tanks, holding water, nutrients, and waste products. They’re especially large in plant cells.
Plasma Membrane: This outer boundary acts as a gatekeeper, controlling what enters and exits the cell. It’s like the city walls, ensuring only the right things get in and out.
Why Ribosomes Don’t Belong
Now, back to the ribosomes. Why are they the odd ones out? It comes down to their structure and function.
Structure: Ribosomes are not bound by a membrane. They are essentially two subunits of RNA and protein that come together to build proteins.
Function: Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell. They read instructions from the nucleus and build proteins based on those instructions. They don’t directly interact with the other members of the endomembrane system.
The Interplay of the Endomembrane System and Ribosomes
While ribosomes might be independent contractors, they do work in close collaboration with the endomembrane system. Here’s how:
1. The nucleus sends out instructions for making proteins to the ribosomes.
2. Ribosomes attached to the rough ER manufacture proteins.
3. The new proteins are then transported to the Golgi apparatus for further processing and packaging.
4. The Golgi apparatus sends out the finished proteins to their destinations, either within the cell or outside.
This collaboration is crucial for the cell’s survival. Imagine trying to run a city without factories, post offices, or recycling centers. It wouldn’t be pretty!
Summary
So, to answer the question directly, the structure that’s not part of the endomembrane system is the ribosome. While ribosomes are essential for protein synthesis, they are free-floating particles and don’t have a membrane like the other structures within the endomembrane system.
This fascinating system highlights the intricate organization of cells, demonstrating how different structures work together to keep life humming along.
FAQs
Q: What is the endomembrane system?
A: The endomembrane system is a group of interconnected organelles in eukaryotic cells, including the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and plasma membrane. These organelles work together to carry out a variety of cellular functions, such as protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and waste disposal.
Q: Why is the ribosome not part of the endomembrane system?
A: The ribosome is not bound by a membrane, unlike the other structures in the endomembrane system. It is a free-floating particle responsible for protein synthesis.
Q: What are some other structures found in the cytoplasm?
A: The cytoplasm contains other structures besides ribosomes, such as mitochondria, which are the powerhouses of the cell, and cytoskeletal elements, which provide support and structure to the cell.
Q: How does the endomembrane system work with ribosomes?
A: The endomembrane system works in collaboration with ribosomes to produce and transport proteins throughout the cell. Ribosomes attached to the rough ER manufacture proteins, which are then processed and packaged by the Golgi apparatus and sent to their final destinations.
Q: What is the significance of the endomembrane system?
A: The endomembrane system is vital for the survival of eukaryotic cells. It enables the cell to perform essential functions, such as protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and waste disposal. The endomembrane system also helps to maintain the cell’s internal environment and structure.
Chapter 6 Practice Test Questions Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which Quizlet
4.4: The Endomembrane System – Biology LibreTexts
In addition to their role as the digestive component and organelle-recycling facility of Biology LibreTexts
5.9: The Endomembrane System – Biology LibreTexts
The endomembrane system (endo = within) is a group of membranes Biology LibreTexts
Endomembrane system – Definition and Examples – Biology Online
The endomembrane system is a system of membranous components. It Biology Online
4.4: The Endomembrane System and Proteins – Biology LibreTexts
Although not technically within the cell, the plasma membrane is included in the Biology LibreTexts
The Endomembrane System – Fundamentals of Cell Biology
There are several membrane-bound organelles that work together to form the Open Educational Resources
4.4 The Endomembrane System and Proteins – OpenStax
Although not technically within the cell, the plasma membrane is included in the OpenStax
Endomembrane system (video) | Khan Academy
The endomembrane system in eukaryotic cells includes cell membrane, nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, vacuoles, and lysosomes. These parts, made of phospholipid bilayers, work together for protein and lipid Khan Academy
Chapters 6-7 (Mastering Biology Questions) Flashcards | Quizlet
Smooth ER is part of the endomembrane system of the eukaryotic cell, and rough ER is Quizlet
Endomembrane System | Structure Of A Cell | Biology | Khan Academy
Which Of The Following Are Not Considered As The Part Of Endomembrane System? A. Mitochondria
Biology: Cell Structure I Nucleus Medical Media
Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure \U0026 Function
The Endomembrane System
The Cell 6- The Endomembrane System
Endomembrane System | The Fundamental Unit Of Life | Biology | Khan Academy
Which Organelle Is Not A Part Of The Endomembrane System ?
Link to this article: which structure is not part of the endomembrane system.
See more articles in the same category here: https://bmxracingthailand.com/what
